Introduction
Artificial intelligence continues to transform the global Technological landscape at a breathtaking velocity. In 2026, DeepSeek has become a foremost name in open‑source AI innovation. But developers, solution architects, business leaders, and AI researchers frequently ask:
Which is superior, DeepSeek‑LLM or DeepSeek‑MoE?
Both frameworks carry common branding, ambitious large‑model strategies, and an open‑community ethos, yet they are structurally divergent. Comprehending these contrasts is indispensable for anyone building AI products, API services, or large‑scale deployment frameworks.
This comprehensive treatise will elucidate:
- Architectural divergences (Dense vs Sparse MoE)
- Performance benchmarks (reasoning, coding, mathematics)
- Economic efficiency & practical deployment considerations
- Real‑world application domains
- Strengths & limitations of each model
- Strategic recommendations based on distinct scenarios
By the conclusion of this exhaustive analysis, you’ll be equipped with the insights you need to determine which model best aligns with your ambitions and infrastructure constraints.
Why DeepSeek Models Matter in 2026
The AI domain has evolved beyond simplistic metrics like raw parameter count. In 2026, the emphasis is on:
- Efficiency per generated token
- Inference expenditure
- Reasoning fidelity for practical task solving
- Horizontal scalability across multiple GPUs
- Deployment cost economics
DeepSeek explores two fundamental architectural paradigms:
- Dense Large Language Models (DeepSeek‑LLM)
- Sparse Mixture‑of‑Experts Networks (DeepSeek‑MoE)
Both aim to deliver high performance and flexibility, but they solve different operational challenges. Selecting the right paradigm can conserve millions in GPU costs and drastically elevate AI dependability.
What Is DeepSeek‑LLM?
Architecture & Conceptual Philosophy
DeepSeek‑LLM employs a dense transformer architecture. In dense networks:
- Every parameter is activated for each token
- Every forward pass engages the entire neural network
- The compute requirement per token remains constant
Think of a 67‑billion‑parameter model: all 67B weights contribute to the generation of each token. This methodology mirrors classical LLM design, akin to Transformer systems in GPT architectures.
Fundamental Traits
| Characteristic | DeepSeek‑LLM |
| Parameter Activation | 100% utilized every token |
| Inference Stability | Highly predictable |
| Hardware Demands | Substantial |
| Scaling Profile | Linear cost scaling |
| Reasoning Consistency | High |
Key Advantages:
Complete parameter engagement
The entire neural infrastructure contributes to every decision.
Stable and deterministic inference
Results exhibit predictable quality across varied inputs.
Strong logical reasoning behaviour
Excellent for deep cognitive reasoning pipelines.
Key Drawbacks:
Elevated GPU memory footprint
Dense models often require high‑end hardware.
Linear cost scaling
Each token costs the same computationally, leading to higher expenditures.
Because every neuron in the network participates in each token generation, DeepSeek‑LLM yields uniform results across diverse tasks — particularly complex reasoning and multi‑step problem‑solving.
Performance Benchmarks
Let’s explore how DeepSeek‑LLM performs across critical tasks:
Reasoning Datasets
In standardized reasoning benchmarks, DeepSeek‑LLM exhibits superior logical problem‑solving ability. Its full activation ensures that knowledge is aggregated coherently across every transformer layer.
Mathematical Reasoning (e.g., MATH benchmark)
Dense architectures demonstrate higher reliability when solving intricate mathematical problems that require multi‑stage reasoning.
Coding Tasks (HumanEval‑style)
DeepSeek‑LLM’s comprehensive model engagement leads to consistent code generation, especially for nested logic or recursive implementations.
Long‑Form Text Generation
Owing to stable context propagation, DeepSeek‑LLM excels in composing comprehensive essays, reports, and structural narratives.
Why Dense Models Excel in Reasoning
In dense systems:
- The entire parameter set assesses each token
- Knowledge propagation is thorough
- Dependencies across distant tokens are integrated seamlessly
This ensures stability in multi‑step reasoning and reduces the risk of route miscalculations during inference.
Use Cases Where DeepSeek‑LLM Shines
DeepSeek‑LLM is particularly potent in scenarios that demand:
- Legal document generation
- Academic research synthesis
- Complex software development assistance
- Structured reasoning pipelines
Strengths of DeepSeek‑LLM
| Strength | Explanation |
| Consistent output quality | Every parameter participates in predictions |
| Strong chain‑of‑thought reasoning | Excellent stability in logical sequences |
| Reliable long‑context comprehension | Better memory for extensive documents |
| Predictable adaptation during fine‑tuning | Dense models change behaviour gradually |
| Stable inference costs per token | Consistent performance metrics |
Limitations of DeepSeek‑LLM
| Limitation | Explanation |
| High inference expenditure | The entire network engages for every token |
| Larger GPU memory requirements | Not suitable for lightweight infrastructure |
| Slower at scale | Efficiency constraints for ultra‑high throughput systems |
| Poor fit for API‑heavy deployments | Higher cost per token under heavy load |
What Is DeepSeek‑MoE?
Mixture‑of‑Experts (MoE) Architecture
DeepSeek‑MoE adopts a sparse activation strategy, activating only a subset of parameters for each token. The model comprises multiple “experts”, with a router mechanism that determines which experts should process each input.
Sparse Activation Example
| Total Parameters | Active per Token |
| 16B | ~2.7B |
This leads to drastic reductions in compute requirements without sacrificing the capacity of a large model.
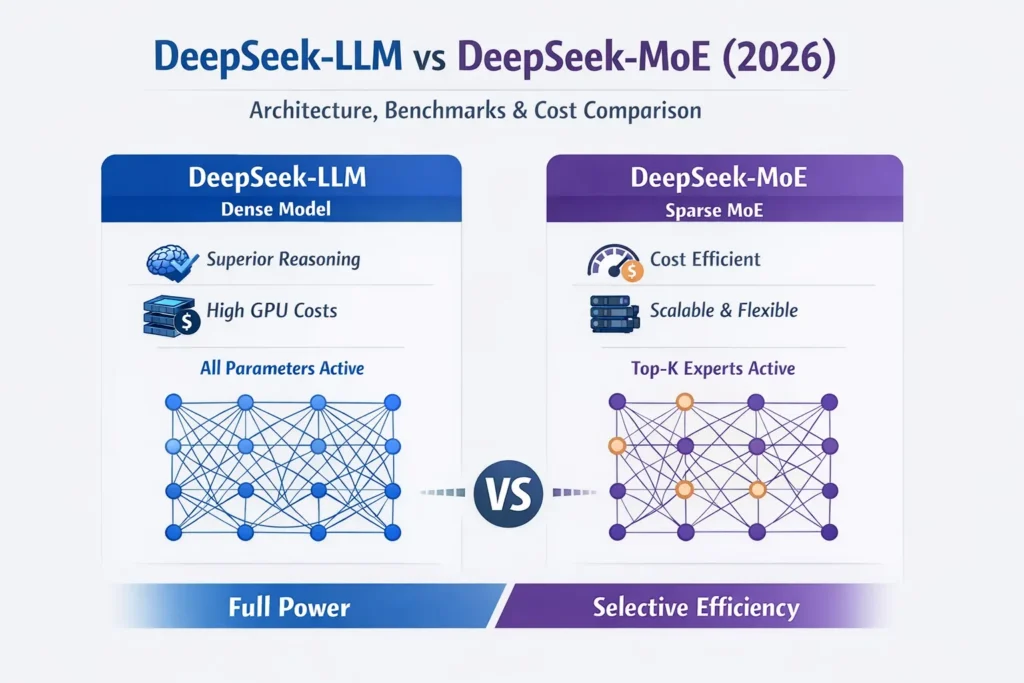
How Expert Routing Works
The expert selection process involves:
- Input token enters the transformer
- A gating network scores all available experts
- Top‑K experts are activated for that token
- Outputs from selected experts are merged
Benefits
Lower computational expenditure
Only a fraction of the model runs for each token.
Enhanced scalability
Efficient parallelization across GPU clusters.
Cost‑effective for large‑scale API deployments
High throughput with lower per‑token cost.
Thus, MoE models provide a “large‑model feel” with a fraction of the runtime compute cost of a full dense model.
Efficiency Benefits
DeepSeek‑MoE is ideal for:
- Lower inference expenses
- High‑throughput AI services
- Enterprise‑grade deployments
- Cost‑sensitive inference systems
For businesses that process millions of requests daily, MoE yields significant financial savings.
Real‑World Applications of DeepSeek‑MoE
MoE architectures are especially suitable for:
- Massive chatbot infrastructures
- SaaS AI integrations
- Enterprise workflow automation
- Scalable customer care AI
- Multi‑tenant API services
DeepSeek‑LLM vs DeepSeek‑MoE — Head‑to‑Head Comparison
Architectural Comparison
| Criteria | DeepSeek‑LLM | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| Architecture | Dense Transformer | Sparse MoE |
| Parameter Activation | Full | Partial (Top‑K) |
| Compute Cost | High | Lower per token |
| Memory Utilization | High | Moderate |
| Scalability | Linear | Highly scalable |
| Routing Complexity | None | Gating mechanism |
Performance Comparison
Reasoning, Coding, Mathematics
| Task Type | DeepSeek‑LLM | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| Complex Reasoning | Excellent | Very Good |
| Coding (HumanEval) | Strong & Predictable | Competitive |
| Mathematical Reasoning | High Stability | Slight Variability |
| Long‑Form Text Generation | Strong Coherence | Efficient but less steady |
| High‑Throughput Chat | Costly | Ideal |
Pros & Cons
DeepSeek‑LLM Pros
- Superior reasoning consistency
- Full parameter intelligence
- Stable fine‑tuning behaviour
- Strong multi‑step logical performance
- Ideal for research & enterprise analysis
DeepSeek‑LLM Cons
- High infrastructure cost
- GPU‑intensive
- Less scalable for massive API loads
DeepSeek‑MoE Pros
- Lower inference expenditure
- Highly scalable computing
- Handles large volumes of requests
- Improved cost‑performance ratio
- Friendly for enterprise deployment
DeepSeek‑MoE Cons
- Routing introduces variability
- More complex to fine‑tune
- Possible imbalance between experts
- Inference behaviour is slightly less stable in logic tasks
Dense vs Sparse: Core Difference
Dense (DeepSeek‑LLM):
Every expert participates in processing all inputs — thorough but costly.
Sparse (DeepSeek‑MoE):
Only relevant experts compute for each token — efficient and scalable.
Neither is universally better; the optimal choice depends on your operational priorities.
Cost & Deployment Considerations
GPU & Infrastructure Requirements
| Model | GPU Requirement | Cost per Token | Ideal Use |
| DeepSeek‑LLM | High | Expensive | Research, Legal, Academic |
| DeepSeek‑MoE | Moderate | Lower | Enterprise APIs, High‑throughput SaaS |
Cost Efficiency Table
| Deployment Scenario | Best Choice |
| Startup with a limited GPU budget | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| Research lab exploring deep cognition | DeepSeek‑LLM |
| Enterprise AI API | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| High‑precision reasoning tasks | DeepSeek‑LLM |
| Cost‑optimized cloud AI | DeepSeek‑MoE |
Use Case Matrix: Who Should Use What?
| Need | Recommended Model |
| Deep logical reasoning | DeepSeek‑LLM |
| Mass customer chatbot | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| Academic research systems | DeepSeek‑LLM |
| Budget‑friendly scaling | DeepSeek‑MoE |
| Coding assistant with cost constraints | Depends on priorities |
Common Misconceptions
MoE is always superior.”
MoE offers efficiency, but accuracy and stability depend on the use case.
Dense always wins accuracy.”
While dense is consistent, modern MoE narrows performance gaps considerably.
Architecture doesn’t influence outcomes.”
The underlying structure profoundly affects cost, scalability, and inference behaviour.
FAQs
A: DeepSeek‑LLM is reliably consistent for high‑precision code tasks, but DeepSeek‑MoE offers competitive outputs at a significantly reduced cost.
A: MoE shines in high‑volume environments with cost efficiency and scalable throughput.
A: For large‑scale enterprise workloads, DeepSeek‑MoE delivers a superior ROI due to lower inference costs.
A: It is feasible but entails greater complexity due to the expert selection mechanisms.
Conclusion
Both DeepSeek-LLM and DeepSeek-MoE present distinct strengths and limitations. Your decision should be driven by:
- Precision & reasoning needs: DeepSeek‑LLM
- Scalability & cost efficiency: DeepSeek‑MoE
For AI developers, research labs, SaaS platforms, and enterprise architects, understanding these nuances enables smarter infrastructure decisions, Improved user experiences, and significant cost savings.