Introduction
Deciding between Llama 2 13B and Llama 2 70B is not about picking the larger model. This result impacts things like the cost of working computers, how long you wait for answers, the number of efforts you can run together, how complicated the setup is, and the overall return on your money, in the long term.
Since Meta AI released the Llama 2 family, people who make things and big companies have always asked:
Is Llama 2 70B truly worth the additional cost over 13B?
We will analyze:
- Parameter scaling and architecture
- Benchmark performance (MMLU, reasoning, coding)
- Inference speed and latency trade-offs
- Hardware and GPU requirements
- Cloud and infrastructure cost modeling
- Real-world deployment use cases
- Production strategies
- A clear decision framework
- A final expert conclusion
Let’s begin with the foundation.
Understanding Llama 2 Architectural Overview
Llama 2 is an open-weight transformer-based large language model suite trained using autoregressive next-token prediction. It was pretrained on extensive publicly available datasets and fine-tuned using supervised instruction tuning and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
The model family includes:
- 7B parameters
- 13B parameters
- 34B parameters (limited release)
- 70B parameters
The most practical commercial comparison is between 13B and 70B because:
- 13B = High performance with manageable infrastructure
- 70B = Maximum reasoning capability with enterprise-level compute
Both share:
- Transformer decoder-only architecture
- 4,096-token context window
- Instruction-tuned chat variants
- Quantization compatibility (4-bit, 8-bit)
- Support for LoRA and parameter-efficient fine-tuning
The core difference lies in parameter count:
- 13B → 13 billion parameters
- 70B → 70 billion parameters
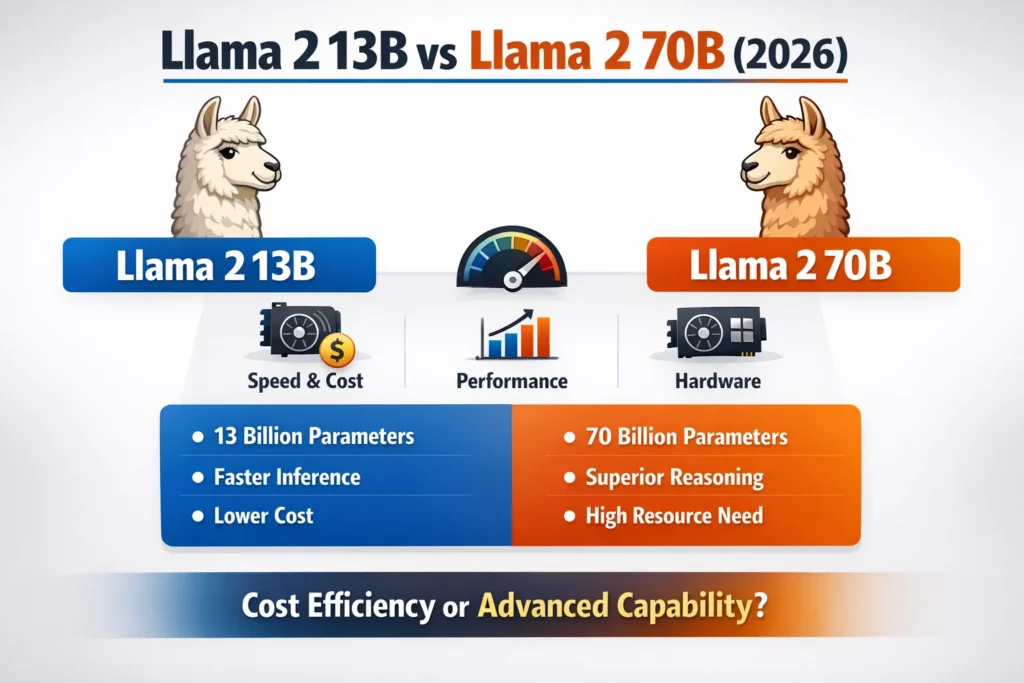
Quick Comparison Table
| Feature | Llama 2 13B | Llama 2 70B |
| Parameters | 13 Billion | 70 Billion |
| Context Window | 4K tokens | 4K tokens |
| Benchmark Performance | Moderate–High | Very High |
| Inference Speed | Faster | Slower |
| GPU Requirement | 24–32GB VRAM | 80GB+ or Multi-GPU |
| Deployment Cost | Lower | High |
| Ideal Use Case | SaaS, chatbots, RAG | Enterprise reasoning, advanced AI |
Performance Benchmarks – Measurable Differences
MMLU & General Knowledge
On the Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark:
- 70B significantly outperforms 13B
- Gains range between 10–20+ percentage points
- Especially strong in STEM and law domains
Why?
Because larger models:
- Encode deeper latent representations
- Capture long-range dependencies more effectively
- Reduce shallow pattern-matching errors
- Improve multi-step reasoning chains
If your system depends on high-accuracy academic reasoning, 70B provides measurable advantages.
However, performance gains are not linear with parameter scaling.
Complex Reasoning Tasks
In domains like:
- Legal document review
- Financial modeling
- Clinical Q&A
- Multi-hop reasoning
- Agent planning systems
70B demonstrates:
- Stronger logical consistency
- Better instruction following
- Reduced contradictions
- Higher structural coherence
13B performs well for structured prompts but may struggle in high-ambiguity scenarios.
For mission-critical systems, 70B offers more reliability.
Coding Performance
For code generation:
70B produces:
- Cleaner syntax
- Fewer broken outputs
- Better algorithmic reasoning
- Improved understanding of Dependencies
13B is effective for:
- Basic scripts
- Debugging
- Automation workflows
- SQL and API generation
When combined with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), 13B can compete effectively in enterprise coding workflows.
Speed & Inference Efficiency
Parameter count directly affects computational demand.
Because 70B has over 5× more parameters:
- It requires more matrix operations per token
- It increases VRAM usage
- It produces higher latency
13B provides:
- Faster token generation
- Lower time-to-first-token
- Better concurrency handling
- Improved real-time user experience
Hardware Requirements
Llama 2 13B
Can run on:
- 24–32GB GPU
- Single high-end GPU instance
- 8-bit quantized setups
- Startups
- Private servers
- Budget-sensitive environments
Infrastructure complexity remains manageable.
Llama 2 70B
Typically requires:
- 80GB GPU (e.g., A100 class)
- Multi-GPU distributed inference
- Advanced tensor parallelism
This results in:
- Higher electricity cost
- Larger cloud bills
- More DevOps complexity
For small teams, this can be a major barrier.
Deployment Cost & ROI
| Cost Factor | 13B | 70B |
| GPU Rental | Moderate | Very High |
| Electricity | Low–Medium | High |
| Scaling | Easier | Complex |
| DevOps | Simple | Advanced |
| ROI (Most Businesses) | Strong | Conditional |
For most SaaS and mid-sized businesses, 13B provides the best cost-to-performance ratio.
70B is justified only if improved accuracy produces measurable financial returns.
Real-World Use Cases
Choose 13B If You:
- Build production chatbots
- Need fast inference
- Operate under budget constraints
- Use RAG pipelines
- Deploy locally
Perfect for:
- Customer support AI
- Content generation tools
- Knowledge bots
- Internal enterprise assistants
Choose 70B If You:
- Require maximum reasoning depth
- Work in regulated industries
- Need highly consistent outputs
- Have an enterprise GPU infrastructure
Ideal for:
- Legal AI
- Medical advisory tools
- Advanced coding assistants
- Multi-agent systems
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Faster inference
- Lower cost
- Easier scaling
- Strong for general NLP
- Excellent for RAG
Cons
- Weaker deep reasoning
- Lower benchmark scores
- Less robust in ambiguous contexts
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Superior reasoning
- Higher benchmark performance
- Better instruction adherence
- Greater consistency
- Enterprise-level intelligence
Cons
- Expensive infrastructure
- Slower inference
- Complex deployment
- High operational overhead
Production Strategy
Leading AI teams increasingly use hybrid routing:
- 13B handles high-volume, real-time queries
- 70B processes complex or high-risk tasks
- RAG improves factual grounding
- Quantization optimizes memory
This architecture balances:
- Cost
- Speed
- Accuracy
FAQs
A: While 70B achieves higher benchmark scores and stronger reasoning, 13B often provides better cost efficiency in practical deployments.
A: Fine-tuning improves specialization, but it typically does not eliminate the reasoning disparity between 13B and 70B.
A: For most chatbot implementations, 13B delivers sufficient performance with superior scalability and lower latency.
A: It reduces hallucination frequency compared to 13B but does not fully eradicate generative inaccuracies.
A: 13B is generally the optimal choice for startups due to manageable infrastructure and lower capital expenditure.
Conclusion
The decision between Llama 2 13B and Llama 2 70B is not about choosing the “smarter” model in isolation, but about aligning model capacity with business objectives, Computational budget, and product requirements.
Llama 2 13B excels in:
- Cost efficiency
- Real-time deployment
- Scalable SaaS systems
- RAG-based architectures
Llama 2 70B excels in:
- Deep reasoning
- Complex analytical workflows
- High-stakes domains
For most businesses in 2026, 13B offers the best balance of intelligence, speed, and cost efficiency.